Anticoagulation: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How It Affects Your Meds
When your blood clots too easily, it can lead to strokes, heart attacks, or deadly pulmonary embolisms. That’s where anticoagulation, the medical process of reducing blood clotting to prevent dangerous blockages. Also known as blood thinning, it’s not about making your blood watery—it’s about fine-tuning the body’s natural clotting system to stay balanced. People on anticoagulation aren’t just taking pills; they’re managing a delicate system that affects everything from surgery recovery to daily activities like falls or dental work.
Anticoagulation doesn’t happen in a vacuum. It connects directly to other meds you might be on. For example, NSAIDs, common painkillers like ibuprofen that can increase bleeding risk when mixed with blood thinners, are a major concern. So are antidepressants, some of which can alter how your body processes anticoagulants, and even corticosteroids, used for inflammation but known to raise clotting risks in some cases. These aren’t side notes—they’re real interactions that can change your safety. That’s why knowing your full med list matters more than ever.
Anticoagulation also ties into how you get your meds. If you’re on a long-term blood thinner, pharmacy delivery or a 90-day supply isn’t just convenient—it’s critical for sticking to your schedule. Missing a dose can spike your clot risk. And if you’re switching generics, you need to know about FDA Therapeutic Equivalency Codes, the system that tells pharmacists which generics can safely replace each other. Not all blood thinners are interchangeable, even if they look the same.
What you’ll find here aren’t just generic guides. These are real stories and practical checks from people managing anticoagulation alongside other conditions—like high blood pressure, chronic pain, or mental health meds. You’ll see how cold exposure might affect your circulation, why sleep changes from antidepressants could mess with your dosing rhythm, and how switching to generics can cut costs without cutting safety. This isn’t theory. It’s what works when you’re living with a blood thinner every day.
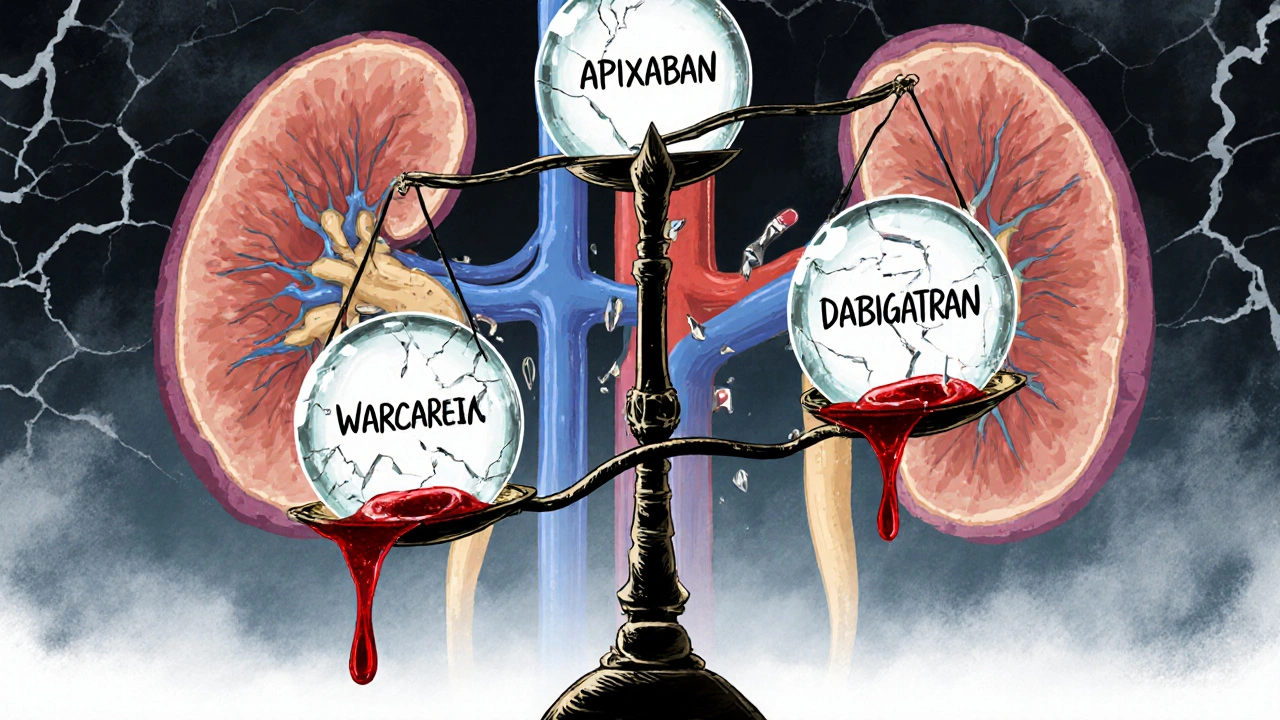
Anticoagulation in Kidney and Liver Disease: What Doctors Really Do
Managing blood thinners in kidney and liver disease is complex. Apixaban is often the safest DOAC, while warfarin remains tricky due to unreliable INR. Real-world data guides decisions when trials don’t.